With @sidbh’s help I was able to rewrite the standard bootloader (and then upload ArduPilot) to an autopilot so I’d like to share how it was done.
- Purchase an STLinkv2 (search on amazon)
- Ensure you have an ArduPilot build environment setup
- If using Windows PC running WSL2 (and VSCode) as I do then you will need to download and install WSL USB Manager to allow WSL2 to access the PC’s USB ports
- Open the Cube’s carrier board and connect to the STLink as shown below
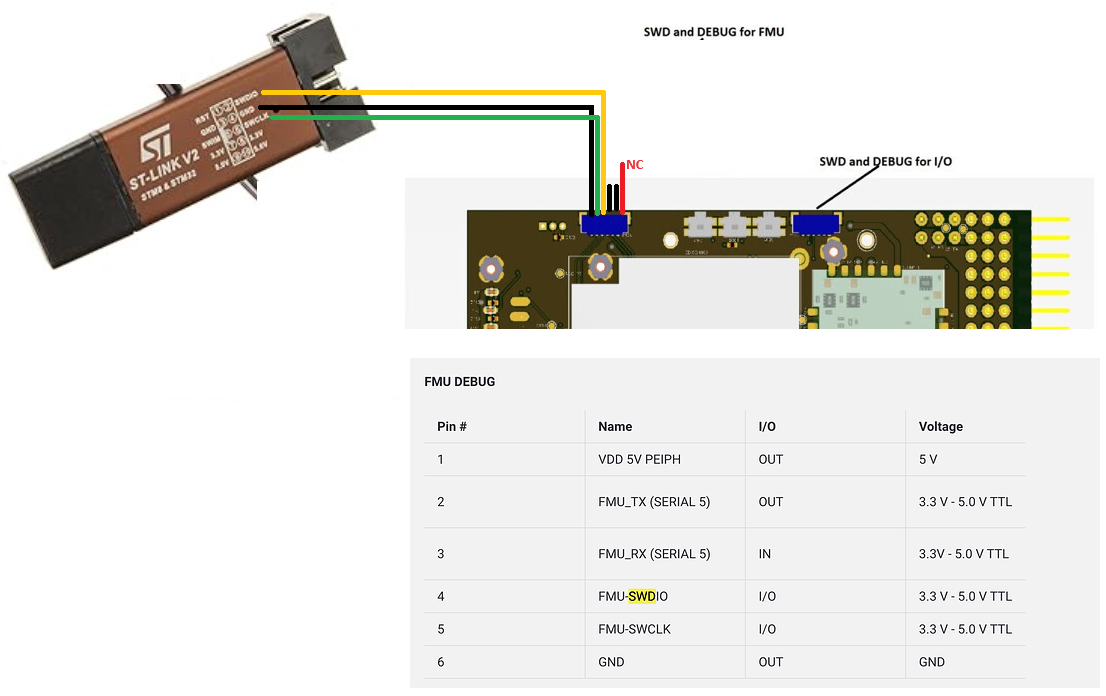
- Connect both the STLinkv2 and Cube to the PC via USB
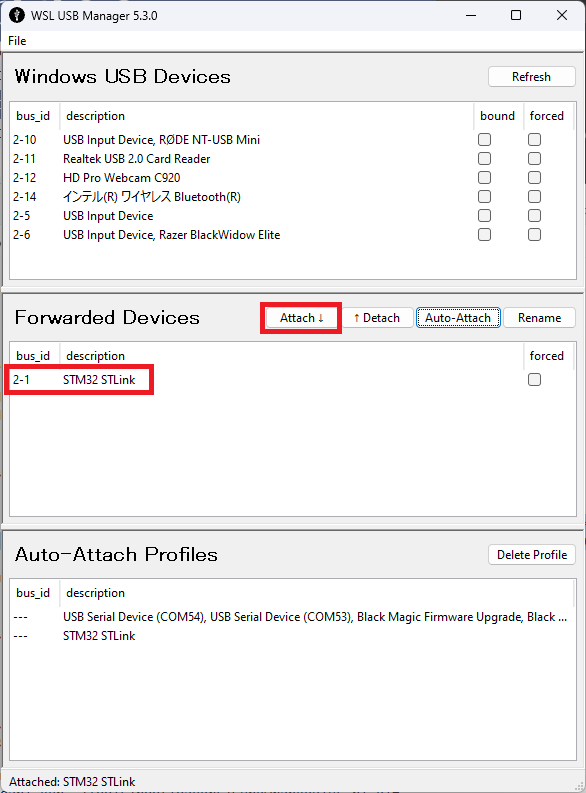
- If using a Windows PC use WSL USB Manager to make the STLink’s COM port available to WSL2. SM32 STLink should appear first in the “Windows USB Devices” area. Select it and push the “Attach” button and it should move to the “Forwarded Devices” section
- Open a WSL2 terminal and cd to the ardupilot directory and enter these commands
- sudo apt install libusb
- sudo apt install openocd
- sudo openocd -f Tools/debug/openocd-h7.cfg
- Open a second WSL2 terminal and again cd to the ardupilot directory and enter these commands
- arm-none-eabi-gdb ./Tools/bootloaders/CubeOrangePlus_bl.elf
- target extended-remote :3333
- monitor stm32h7x mass_erase 0
- monitor halt
- load ./Tools/bootloaders/CubeOrangePlus_bl.elf
OR - monitor flash write_image ./Tools/bootloaders/CubeOrangePlus_bl.elf
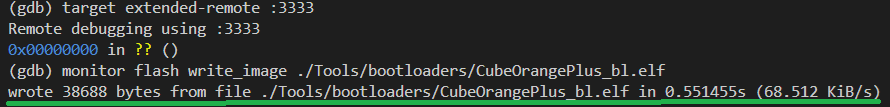
- the commands from above would sometimes work and would sometimes not work. I often had to power cycle the STLink and repeat steps 7 and 8 but eventually I would see a message like below
- power cycle the Cube and use MP to load the software as per usual
By the way, @sidbh said that it is much easier to instead use a JLink programmer and the software that comes with it. The key point is that you need to load the appropriate bootloader (ending in .elf) from this directory onto the board. Once that is done correctly you can use the regular MP or QGC to get AP onto the board.